Story
A strong bond: Overmolding TPEs on polycarbonates for medical wearables
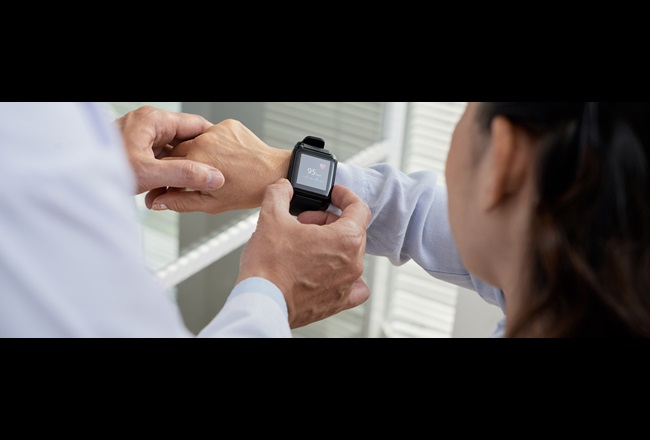
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) and polycarbonates offer a unique combination of rigid and soft materials for housings and interfaces in wearables. To create durable devices that withstand repeated use, these materials must demonstrate strong adhesion and offer chemical resistance.
Combining medical-grade materials for durable devices
Healthcare OEMs often rely on polycarbonates due to their outstanding physical properties and processability. For example, medical-grade resins that meet criteria for skin contact biocompatibility are a top choice for wearable devices.
Thermoplastic Elastomers - TPEs - are more flexible materials and are also available as medical grades and are ideal for gaskets, seals, grips, handles or soft components to provide comfort for wearables.
Polycarbonates and TPEs are often combined by overmolding. This is done by either two-shot or insert molding, in which the two materials can be quickly joined in a molding machine to avoid adhesives or secondary assembly steps.
Putting adhesion and chemical resistance to the test
In a recent study, we evaluated the adhesion of Teknor Apex’s Medalist® medical-grade TPEs—which are designed for overmolding—on various medical-grade polycarbonate substrates. Peel strength measurements on overmolded test pieces of Makrolon® polycarbonate, Bayblend® PC+ABS and Makroblend® PC+polyester alloys showed strong adhesion to several Medalist® TPE grades. All failures during peel tests showed cohesive failures, while we saw slightly higher peel strengths with direct two-shot overmolding than with insert molding.
Wearable devices are frequently cleaned and often come into contact with skin creams or lotions that may degrade plastics. With this in mind, chemical resistance is key—so we also looked at how TPE and polycarbonate substrates stood up to isopropyl alcohol and suntan lotion. Chemical resistance tests suggest that Medalist® MD-36975 and Makrolon® 2458 polycarbonate are excellent choices for wearable devices.
Learn more about the adhesion of TPEs on polycarbonates for medical wearables in our technical paper, published in collaboration with Teknor Apex.
Bayblend®, Makroblend® and Makrolon® are registered trademarks of the Covestro Group. Medalist® is a registered trademark of the Teknor Apex Company.
Polycarbonates and thermoplastic elastomers offer a unique combination of rigid and soft materials for housings and interfaces in medical wearables. To create durable devices that can withstand repeated use, there must be a strong adhesion between these materials. Teaming up with Teknor Apex to examine combinations important to wearable devices was a valuable opportunity and experience, and also provided much-needed technical data for our customers.
Key Benefits
- Chemical resistance Medalist® MD-36975 and Makrolon® 2458 withstand suntan lotion and isopropyl alcohol.
- Strong adhesion Overmolded polycarbonates show strong adhesion to various TPE grades.
- Biocompatibility Medical-grade polycarbonates meet criteria for skin contact biocompatibility.