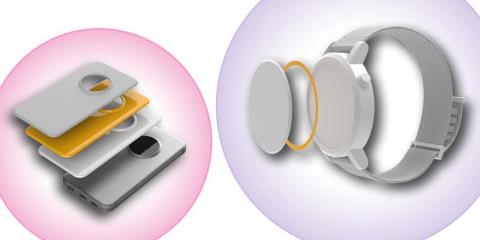
TPU and polycarbonate films solutions enable printed electronics
Whether in sensors, modern control panels, and smart packaging, printed electronics have become an integral part of everyday life. Modern technology and materials allow designers to create interfaces and devices that are not merely appealing but also lightweight, seamless, durable and highly functional.
Innovative substrates and conductive inks
Printed electronics have the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and use electronic devices, making them more accessible. But how does that work?
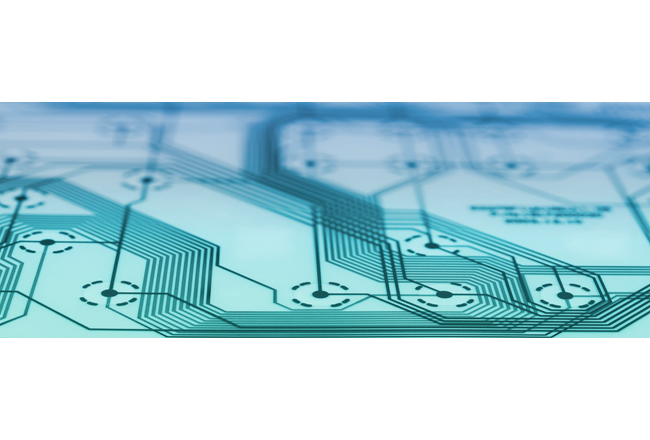
Printed electronics use printing methods to create electrical HMI (Human Machine Interface) devices on different types of materials, known as substrates. This technology involves the use of conductive inks, pastes, and other materials that can be printed onto a variety of surfaces and substrates. Typically standard printing techniques and conventional printing equipment, such as screen printing or inkjet printing are used.
The key component of printed electronics are functional inks based on innovative materials. The inks and printing techniques create a technology that allows for design freedom, lower cost and greater flexibility and production speed. Not only standard inks but copper and silver-based inks, too, can be used in printing processes involving thermoplastic films. Printing with copper and silver-based inks ensures good conductivity and allows sensor technology to be integrated more reliably.
Substrates can be either rigid or highly flexible. Covestro offers a wide range of engineering films to cater to different needs for a variety of applications. The Specialty Films portfolio comprises of Makrofol® Polycarbonate (PC) Films for applications, where a rigidity, stiffness and a lightweight design is required, and Platilon® Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) films for very flexible applications. Also, our thermoplastic films can be used to encapsulate and protect printed electronic components, such as conductive inks or sensors. They act as a barrier against moisture, dust, and other external factors that may affect the performance and longevity of the printed electronics.
Flexible, stretchable, lightweight – TPU films in printed electronic
A wide range of printed electronics applications, such as in textile and sports equipment, smart patches, automotive seating with integrated functions require a more flexible material. Our Platilon® TPU film grades provide mechanical flexibility, allowing the final product to bend and conform to different shapes or surfaces, enabling the development of wearable electronics or flexibles. TPU films with stretchable properties can be used to create stretchable circuitry. This is particularly useful in applications where the printed electronics need to maintain functionality while being stretched or deformed, such as in smart textiles or flexible healthcare devices, steering wheel & seat heating.
Not only can the TPU films be printed with standard inks, but they also show good printability with silver-based inks. Printability with silver-based inks is important as it ensures good conductivity and allows sensor technology to be integrated more reliably. This makes them particularly suitable for medical and healthcare applications.
Our TPU films can also serve as adhesive layers to bond different layers of printed electronics or to attach them to other substrates, such as fabrics or plastic surfaces. The adhesion properties of elastomers help provide a strong and reliable bond between various components.
Slim and robust – Polycarbonate/Thermoplastic Films for Printed Electronics
In-mold electronics (IME) integrate printed electronics and circuitry with 3D thermoforming and molding to create three-dimensional objects with embedded circuits. IME allows designers to develop thinner and more lightweight products that are also visually more appealing.
The films are subsequently shaped to comply with the design of the molded surfaces of the final product. The formed film is loaded into a custom plastic injection molding tool and then over-molded to integrate all circuitry and graphics. Additional surface printing of the circuitry and graphics allows designers to incorporate touch controls and lighting using conventional in-mold decoration manufacturing methods.
With the ability to integrate decorative graphics, lighting, and a host of other features, this truly transformative technology is bound to span across industries. By stripping away the mechanical buttons found in conventional electronics, by giving designers unprecedented freedom to create elegant user experiences through minimalistic interfaces, and by seamlessly integrating electronics into sleek and stylish surfaces, in-mold electronics open up a whole new world of enhancements and human-machine interfaces (HMI).
Film insert molding (FIM) enables one-step fabrication of plastic components with a decorated or functional surface. In this process, a plastic film, usually decorated by printing on the back, is shaped and trimmed before being placed in an injection mold and back-injected or over-molded with a thermoplastic resin.
Key Benefits
- Lightweight and slim: Enable significant weight reduction and part thickness.
- Robust: Provide strong mechanical structure.
- Design freedom: Enable individual design and seamless surfaces.
- Versatile: The potential functions and applications are virtually unlimited.
- Efficient processing: Conventional printing processes are applicable.