Processing technology
Digital engineering simulation: Improving design and production efficiencies
Whenever technical solutions for current and future applications are required, design engineers can rely on computer-aided engineering (CAE) methods to significantly improve efficiency in the design, function and production of thermoplastic parts – saving time and money.
Featured Brands
- Apec® is Covestro brand for high-performance polycarbonate specialties, addressing complex requirements through advanced technology.
- Versatile toughness via blends of PC+ABS; PC+ASA; ABS+PC and PC+SAN
- Smart combinations of polycarbonate and polyester in ultra-tough materials
- High-performance polycarbonate for applications in diverse industries.
Our Digital Engineering team is your partner in simulation for concept evaluation, technology development and project support to optimize part design and processing. This approach avoids multiple iterations of trial and-error in the design and engineering process, and ultimately provides customers with a faster, and trouble-free, path to commercialization.
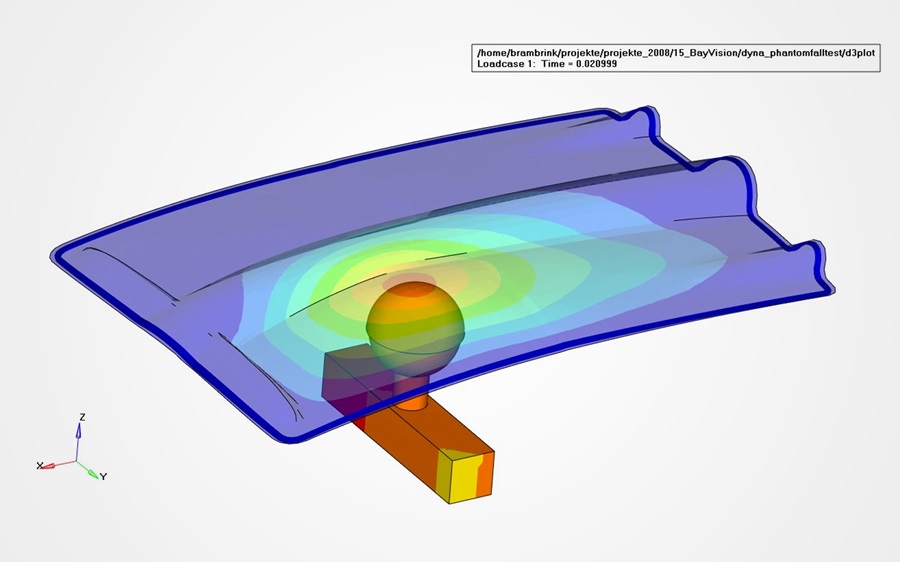
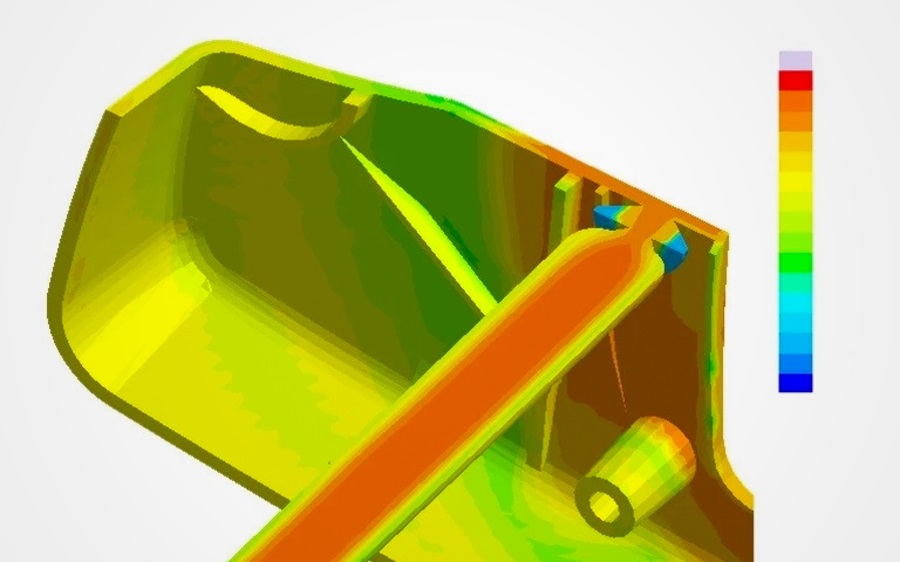
Through the use of digital simulation tools for injection molding as well as structural and thermal analysis, design engineers can gather more specific insights for a particular part and production process to further refine and optimize design and production metrics such as quality, rate, etc. The results of CAE analysis lead to a better understanding of physical relations within the part, a significant reduction in the number of prototype parts required, increased product development speed, and assistance in determining the optimal part design.
Since CAE cannot account for all variables, designers use physical testing for verification. We use our own injection molding and test lab for material data and processing validation. Additionally, we conduct physical tests to characterize the dynamic (high rate) behavior of our materials which can be used in crash analyses. We utilize a broad range of state-of-the-art CAE software programs, including Autodesk Moldflow, ABAQUS or LS-DYNA, to perform injection molding simulations and structural analysis. Furthermore, we can simulate a range of physics problems such as heat transfer, fluid dynamics (CFD), micro-mechanics for composites, photometrics for lighting and optical analysis for customized illumination effects.
Through the use of digital simulation tools for injection molding as well as structural and thermal analysis, design engineers can gather more specific insights for a particular part and production process to further refine and optimize design and production metrics such as quality, rate, etc. The results of CAE analysis lead to a better understanding of physical relations within the part, a significant reduction in the number of prototype parts required, increased product development speed, and assistance in determining the optimal part design.
Since CAE cannot account for all variables, designers use physical testing for verification. We use our own injection molding and test lab for material data and processing validation. Additionally, we conduct physical tests to characterize the dynamic (high rate) behavior of our materials which can be used in crash analyses. We utilize a broad range of state-of-the-art CAE software programs, including Autodesk Moldflow, ABAQUS or LS-DYNA, to perform injection molding simulations and structural analysis. Furthermore, we can simulate a range of physics problems such as heat transfer, fluid dynamics (CFD), micro-mechanics for composites, photometrics for lighting and optical analysis for customized illumination effects.
Injection molding simulation: Optimizing thermoplastics part design & production
Injection molding simulation software helps you verify and optimize polycarbonate part and mold designs by providing visual and numerical feedback aimed at identifying potential problems that may occur during the injection molding process. CAE simulation software reduces the need for costly physical prototypes, avoids manufacturing defects, lowers scrap rates, and reduces time to market. As technologies advance, so do CAE simulation capabilities for injection molding. CAE software allows designers to visualize the predicted quality of optical lenses using 3D simulation. It is also possible to detect and troubleshoot shrinkage and warpage to save time and avoid unnecessary costs. To more fully support your projects, we provide advanced material data for rheological simulations, including pressure-dependent viscosity, which is a key property for polycarbonate- based products.
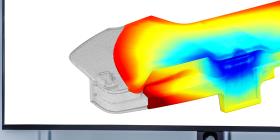
Structural, thermal and light & optics analysis for new technology and application development
Certain aspects of structural design are particularly relevant to thermoplastics. Structural analysis is therefore an essential step in the design process for thermoplastic parts. This step relies on CAE software tools to determine the ability of a part or assembly to withstand applied loads. When designing thermoplastic parts, it is important for to consider not only the magnitude of mechanical loads but also their type (tensile, compressive, multi-axial, etc.) and duration. Unlike metals or alloys, thermoplastics can exhibit dramatically different behavior depending on whether a load is instantaneous, long-term, or recurring (e.g. vibrational loads). Temperature and other environmental factors can also affect mechanical performance. The complex nature of thermoplastic behavior, including viscoelasticity and process-induced factors, makes predicting the performance of a given part all the more challenging.
In addition to applications involving structural loads, CAE tools have been developed to address new applications such as heat sinks in electronics and LED lighting, where thermal loads are a concern. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations can be used to predict a part’s thermal performance in managing heat in lighting, EE&A or telecommunication (5G) applications.
In addition to applications involving structural loads, CAE tools have been developed to address new applications such as heat sinks in electronics and LED lighting, where thermal loads are a concern. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations can be used to predict a part’s thermal performance in managing heat in lighting, EE&A or telecommunication (5G) applications.