Technology
Permeability
Our thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) are permeable to gases and liquids. Different grades, building blocks and additives can be used to meet specific permeability requirements.
Featured Brands
- Thermoplastic polyurethanes
Permeability describes the transmission of a medium, usually of a gas, sometimes of a liquid, through a test specimen. The test process for permeability can be divided into three separate stages:
• Entrance of the medium into the test specimen
• Diffusion of the medium through the test specimen
• Escape of the medium from the test specimen
Permeability is directly proportional to the temperature of a test specimen and inversely proportional to the wall thickness. Below you can find an overview of permeability properties for our main TPU materials for different types of gases and fuels.
• Entrance of the medium into the test specimen
• Diffusion of the medium through the test specimen
• Escape of the medium from the test specimen
Permeability is directly proportional to the temperature of a test specimen and inversely proportional to the wall thickness. Below you can find an overview of permeability properties for our main TPU materials for different types of gases and fuels.
Gas permeability
The following table shows the permeability of different gases for some important Desmopan® grades, measured according to DIN 53380, Part 1, for films with a 100 µm thickness.
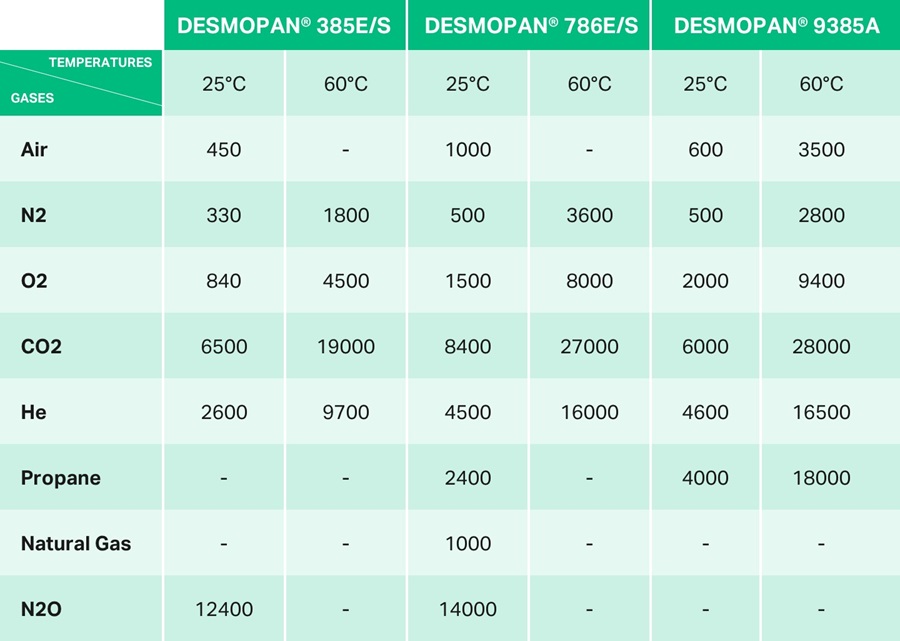
Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) are not generally used as barrier materials. However, polyester TPUs tend to have a lower gas permeability than polyether TPUs, making them more suitable as a barrier material. Additives can also be used to achieve a further reduction in gas permeability. When compounded into the material, they can reduce gas permeability by approximately 30%. If high gas permeability is requested, either polyether-based TPU or a special polycarbonate-based TPU are more suitable choices. The latter category of TPU is especially interesting when increased gas permeability must be combined with resistance to a wide range of chemical substances.
Fuel permeability
The following table shows the fuel permeability (FD) of Desmopan® 786. The measurements were taken according to DIN 53532 on a polyester fabric coated on both sides with a 100 µm layer of Desmopan® 786 and exposed to three different fuels.

Fuel 1 = pure isooctane (2,2,4-Trimethylpentane)
Fuel 2 = blend of isooctane/toluene (70:30 vol.%)
Fuel FAM = blend of pure toluene/isooctane/diisobutylene/pure ethanol (50:30:15:5 vol.%)
Desmopan® 786 is a thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) containing polyether carbonate polyols. It is well-suited for simultaneous contact with fuel and water. Due to the unique formulation of Desmopan® 786, it offers an equally high resistance against fuels and hydrolysis.
Fuel 2 = blend of isooctane/toluene (70:30 vol.%)
Fuel FAM = blend of pure toluene/isooctane/diisobutylene/pure ethanol (50:30:15:5 vol.%)
Desmopan® 786 is a thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) containing polyether carbonate polyols. It is well-suited for simultaneous contact with fuel and water. Due to the unique formulation of Desmopan® 786, it offers an equally high resistance against fuels and hydrolysis.