Story
Benefits of PU Insulation
Insulation requires space. Just how much depends on the insulating performance of the material used. Rigid polyurethane (PU) foams insulate better than most other conventional insulating materials. That makes thinner solutions possible and creates more living space.
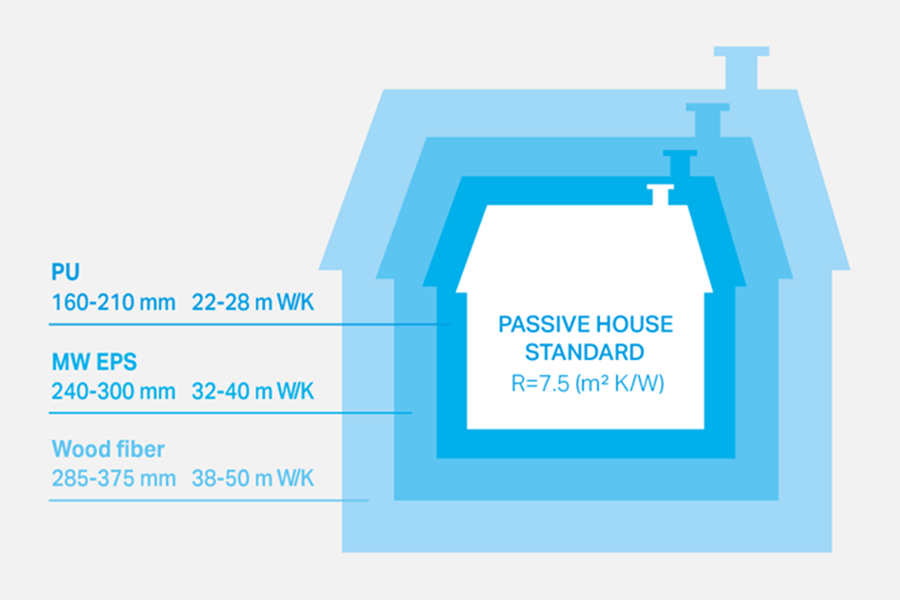
Insulation thickness of different insulation materials
Convincing arguments
PU’s good insulating performance is due to its low thermal conductivity. The gas enclosed in the foam pores is also a major contributing factor. This gas is added during PU production to enhance the performance of the foam. For many applications today the gas is pentane, which has half the thermal conductivity of air.- High insulating performance: Of all today’s conventional insulating materials PU offers the highest insulating performance as it has a much lower thermal conductivity value than insulating materials such as polystyrene, mineral wool, glass wool or hemp. PU with a thermal conductivity rating of 0.23, for example, insulates two-thirds better than some other material with a rating of 0.40.
- More living space: PU enables a thinner insulating layer than other insulation materials and thus a thinner wall. This results in more interior space for new buildings and minimal space requirements for retrofit insulation of older buildings.
- High aging durability: Besides being mechanically durable, moisture- and temperature-resistant and chemically stable, PU displays high aging resistance, typically extending beyond a building’s usual lifecycle.
- Great versatility: Rigid PU panels can be cut to any size using simple tools. Even more design flexibility can be achieved by foaming the insulation material. PU can also be combined with other building materials and incorporated into composite or sandwich panels. PU metal-faced sandwich panels are particularly suitable for efficient commercial and industrial constructions.
- Outstanding energy balance: From a lifecycle perspective PU has an excellent energy balance. PU used in building insulation, for example, saves approximately 70 times more energy over its entire lifecycle than is needed to manufacture it.






.jpg?h=297&w=594&rev=ee8e09106bd14140b4f8ca39945b151e&hash=9D43F4A5BCF50BCE37ACB3CB5EAF07D9&usecustomfunctions=1¢ercrop=1)




